Table of contents
- What is Metabolic Encephalopathy?
- How Metabolic Imbalance Impacts the Brain
- Common Causes of Metabolic Encephalopathy
- Symptoms of Metabolic Encephalopathy
- Diagnostic Approach
- Treatment of Metabolic Encephalopathy
- Prevention Strategies
- Complications of Untreated Metabolic Encephalopathy
- SEO-Friendly Tips for Online Content on Metabolic Encephalopathy
- FAQs About Metabolic Encephalopathy
- Conclusion
Metabolic Encephalopathy health is crucial for every organ in the body; however, the brain is particularly sensitive to even minor changes in metabolism. When the body’s metabolic balance is disrupted, it can lead to serious neurological consequences. One such condition is metabolic encephalopathy, which occurs when metabolic disturbances impair normal brain function. In addition, understanding how metabolic imbalances affect the brain is essential for early detection, prevention, and effective treatment. Consequently, awareness of the causes, symptoms, and management strategies can significantly improve patient outcomes.
This condition refers to a spectrum of brain dysfunction caused by systemic metabolic disturbances. Understanding metabolic encephalopathy is essential for early detection, prevention, and effective management.
In this article, we will explore how metabolic imbalance affects the brain, the causes, symptoms, diagnostic approaches, treatment options, and preventive measures. Additionally, we provide an SEO-friendly structure with frequently asked questions to enhance readability and accessibility.
What is Metabolic Encephalopathy?
Metabolic encephalopathy is a medical condition in which the brain’s normal function is impaired due to systemic metabolic disturbances. Unlike structural brain diseases caused by trauma or stroke, metabolic encephalopathy is functional; in other words, it affects brain activity without causing permanent structural damage, provided it is identified early.
Furthermore, the condition is often reversible if the underlying metabolic imbalance is corrected. Typically, it presents with symptoms such as confusion, altered consciousness, memory deficits, and cognitive dysfunction. Depending on the severity and duration of the metabolic disruption, the symptoms can range from mild confusion to deep coma. Therefore, early recognition and treatment are crucial to prevent long-term complications.
How Metabolic Imbalance Impacts the Brain
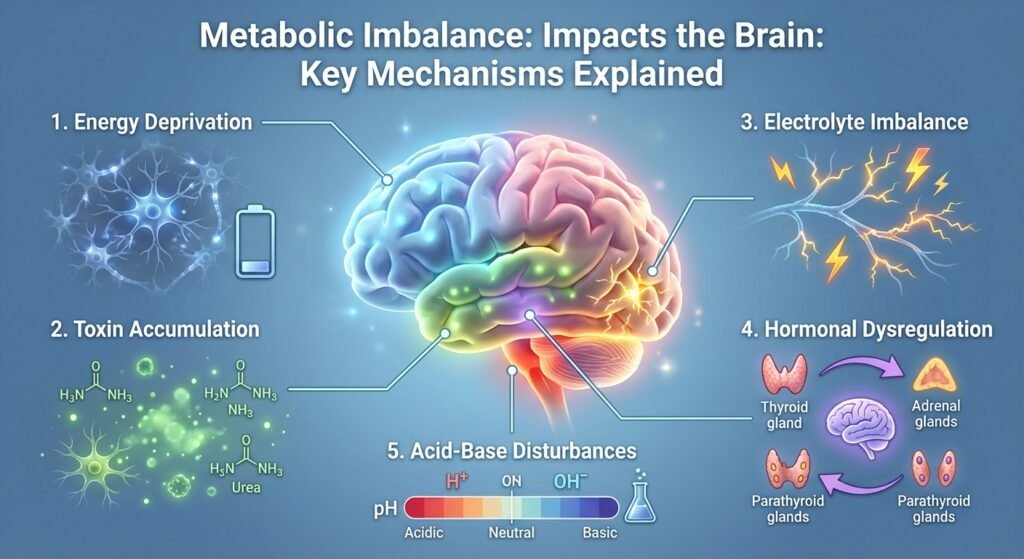
The brain relies on a delicate balance of nutrients, hormones, electrolytes, and waste removal mechanisms to function optimally. Metabolic imbalances can interfere with these processes in multiple ways:
- Energy Deprivation: The brain depends primarily on glucose for energy. Conditions like hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) or severe malnutrition can deprive neurons of energy, leading to impaired cognition and neurological deficits.
- Toxin Accumulation: The liver and kidneys detoxify the body. If these organs fail, toxins like ammonia and urea accumulate, affecting neurotransmission and causing symptoms such as confusion and lethargy. This is often observed in hepatic encephalopathy.
- Electrolyte Imbalance: Sodium, potassium, calcium, and magnesium are essential for neuron function. Imbalances can disrupt electrical signaling, leading to seizures, tremors, or coma.
- Hormonal Dysregulation: Thyroid, adrenal, and parathyroid hormones play a vital role in brain metabolism. Dysregulation can affect mood, memory, and cognitive functions.
- Acid-Base Disturbances: Conditions like metabolic acidosis or alkalosis affect enzyme activity and ion transport in the brain, leading to cognitive dysfunction.
Common Causes of Metabolic Encephalopathy
Metabolic encephalopathy can result from a wide range of systemic disorders. Some common causes include:
- Liver Dysfunction: Chronic liver disease can lead to hepatic encephalopathy, where ammonia and other toxins accumulate in the bloodstream, crossing the blood-brain barrier and disrupting neural activity.
- Kidney Failure: Uremic encephalopathy occurs when waste products like urea build up in the blood due to impaired kidney function.
- Electrolyte Imbalance: Low sodium (hyponatremia), high calcium (hypercalcemia), or low magnesium (hypomagnesemia) can interfere with neurotransmission and neuronal excitability.
- Hypoglycemia and Hyperglycemia: Both low and high blood sugar levels can impair brain function. Severe hypoglycemia may lead to seizures or permanent brain damage if prolonged.
- Severe Infections: Sepsis and systemic infections can trigger inflammatory and metabolic cascades, resulting in septic encephalopathy.
- Medication and Toxins: Certain drugs, alcohol, or toxins can disrupt metabolic processes, contributing to encephalopathy.
- Thyroid and Adrenal Disorders: Hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, or adrenal insufficiency can impair cognition and cause confusion or lethargy.
Symptoms of Metabolic Encephalopathy
metabolic cause and severity but typically include:
- Confusion and disorientation
- Memory loss or difficulty concentrating
- Altered level of consciousness (drowsiness to coma)
- Tremors, muscle weakness, or involuntary movements
- Mood changes, irritability, or depression
- Slurred speech or difficulty communicating
- Seizures in severe cases
Diagnostic Approach
Early diagnosis is essential to prevent permanent brain damage. The diagnostic process typically includes:
- Medical History and Physical Examination
- Identifying underlying metabolic disorders
- Reviewing medications, alcohol use, and recent infections
- Laboratory Tests
- Blood glucose, electrolytes, liver and kidney function tests
- Ammonia and urea levels
- Hormone levels (thyroid, adrenal, parathyroid)
- Neuroimaging
- MRI or CT scans to rule out structural brain lesions
- Electroencephalogram (EEG)
- Detects abnormal brain electrical activity, often helpful in encephalopathy
- Additional Tests
- Depending on the suspected cause, tests like blood cultures, toxin screening, or cerebrospinal fluid analysis may be conducted
Treatment of Metabolic Encephalopathy
Treatment primarily focuses on correcting the underlying metabolic imbalance and supporting brain function:
- Addressing the Cause
- Treat liver or kidney failure
- Correct electrolyte imbalances
- Manage blood sugar levels
- Treat infections aggressively
- Medications
- Lactulose for hepatic encephalopathy to reduce ammonia levels
- Electrolyte supplements or medications to correct imbalances
- Insulin therapy or glucose administration for blood sugar abnormalities
- Supportive Care
- Ensuring adequate hydration and nutrition
- Monitoring vital signs and neurological status
- ICU care for severe cases with risk of coma
- Lifestyle Adjustments
- Avoiding alcohol and toxins
- Maintaining balanced nutrition
- Regular medical checkups for chronic conditions
Prompt intervention often reverses the symptoms of metabolic encephalopathy. However, prolonged or untreated cases can lead to irreversible brain damage, seizures, or even death.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing metabolic encephalopathy revolves around maintaining overall metabolic health and addressing risk factors:
- Monitor Chronic Conditions
- Regular checkups for liver, kidney, thyroid, and diabetes management
- Healthy Lifestyle
- Balanced diet rich in nutrients
- Adequate hydration
- Avoid excessive alcohol or toxic substances
- Medication Management
- Use prescribed medications responsibly
- Avoid self-medication with potentially harmful drugs
- Early Detection of Imbalances
- Regular blood tests to monitor electrolytes, glucose, and liver/kidney function
- Immediate attention to sudden confusion, weakness, or neurological symptoms
Complications of Untreated Metabolic Encephalopathy
If left untreated, metabolic encephalopathy can lead to severe complications:
- Permanent cognitive impairment
- Seizures and neurological damage
- Coma and death in extreme cases
- Complications from the underlying disease, such as liver or kidney failure
Early recognition and treatment significantly improve outcomes and reduce the risk of permanent brain damage.
SEO-Friendly Tips for Online Content on Metabolic Encephalopathy
To make your content discoverable and valuable for readers:
- Use Targeted Keywords:
- Metabolic encephalopathy
- Causes of brain dysfunction
- Symptoms of metabolic imbalance
- Treatment for encephalopathy
- Structure Content Properly:
- Use H1, H2, and H3 tags for headings
- Include bullet points and lists for readability
- Use short paragraphs
- Include FAQs:
- Answer common questions to improve engagement and SEO
- Internal and External Linking:
- Link to related articles, credible health sites, and scientific studies
FAQs About Metabolic Encephalopathy
Q1: Is metabolic encephalopathy reversible?
A: Yes, in most cases, if the underlying metabolic cause is treated promptly, the brain can recover fully without permanent damage.
Q2: What are the most common causes of metabolic encephalopathy?
A: Common causes include liver disease, kidney failure, electrolyte imbalances, hypoglycemia, infections, toxins, and hormonal disorders.
Q3: Can metabolic encephalopathy cause permanent brain damage?
A: If untreated for a prolonged period, it can lead to irreversible cognitive impairment, seizures, or coma.
Q4: How is metabolic encephalopathy diagnosed?
A: Diagnosis involves medical history, physical examination, blood tests, imaging studies, EEG, and sometimes cerebrospinal fluid analysis.
Q5: What treatments are available for metabolic encephalopathy?
A: Treatment focuses on correcting the underlying metabolic disorder, supportive care, medications for symptoms, and lifestyle adjustments.
Q6: Can metabolic encephalopathy occur in children?
A: Yes, children with metabolic disorders, liver or kidney issues, or severe infections can develop metabolic encephalopathy, requiring prompt medical attention.
Q7: How can I prevent metabolic encephalopathy?
A: Preventive measures include managing chronic diseases, maintaining a balanced diet, avoiding toxins, monitoring blood tests, and seeking early treatment for neurological symptoms.
Conclusion
Metabolic encephalopathy is a serious yet often reversible condition caused by systemic metabolic imbalances. Understanding how metabolic disturbances affect the brain is essential for early recognition and effective treatment. Prompt medical intervention can restore brain function and prevent long-term neurological damage.
Maintaining metabolic health through proper nutrition, disease management, and regular medical checkups is crucial for brain wellness. Awareness of the symptoms, causes, and preventive strategies empowers patients and caregivers to act quickly, ensuring better outcomes and healthier lives.


